The rapidly growing global e-mobility industry requires new, innovative flame retardants and demand keeps increasing massively
Compared to classic cars with combustion engines,
more
ECHA Suggestion of classification, labelling and also restriction of selected chlorinated flame retardants paves the way for an increased need for halogen free flame retardants
The European Chemicals Agency ECHA recently propos
more
The Working Group „Flame Retardants“ brings together many participants from the flame retardants value chain and celebrates Prof. Manfred Döring’s well-deserved retirement
Finally, the meeting of the working group “F
more
“ECOFRAM" addresses the need for more sustainable flame retardants and showcases developments from science and industry
The International Conference on Eco-Friendly Flame
more
RoHS: Impact study finds positive results, review process has started
The importance of RoHS, the restriction of hazardo
more
“Fire Resistance in Plastics" addresses the need for flame retardants for e-mobility – halogen-free solutions in clear focus
The Fire Resistance in Plastics is one of the most
more
Phosphorus
Mode of action: formation of a solid charred surface layer of phosphorus compounds and in specific cases interruption of the radical chain process in the gas phase.
Phosphorus-containing flame retardants primarily act in the solid phase of the polymer. The flame retardant is transformed into phosphoric acid by thermal degradation, and water is released from the substrate in the solid phase.
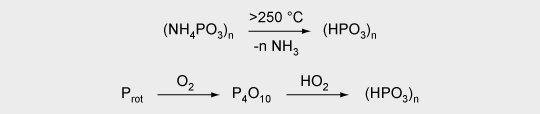
A protective layer is developed by the polyphosphoric acid formed and by subsequent charring. The protective layer consists of interpenetrating networks of carbon and phosphorus oxides.

Specific phosphorus flame retardants such as the metal phosphinates may also act in the gas phase by the formation of P and PO radicals interrupting the radical chain mechanism of the cumbustion process.
Important phosphorus-containing flame retardants are:
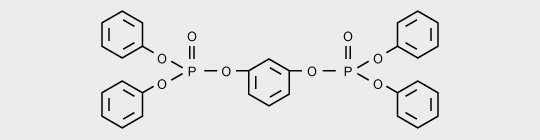
Resorcinol bis (diphenyl phosphate) (RDP) is mainly used to flame retard PC/ABS blends.
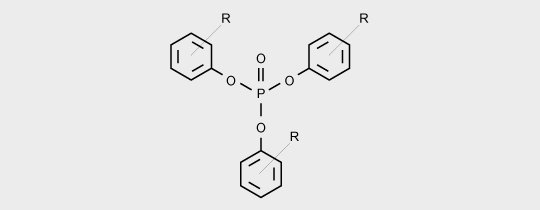
Triaryl phosphates are used for many applications in thermoplastics.
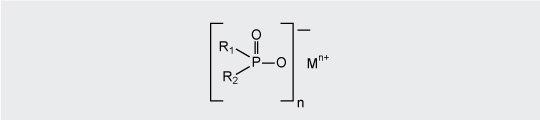
Metal phosphinates are increasingly used in glass fiber reinforced polyamides and polybutylene terephthalate.
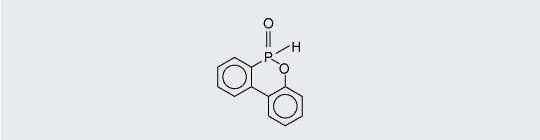
9,10-Dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide (DOPO) and its derivates are used in polyester fibers and increasingly in printed circuit boards.
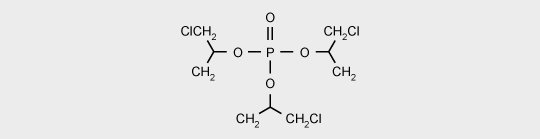
Trischloropropyl phosphate (TCCP) is mainly used in polyurethane flexible foams.
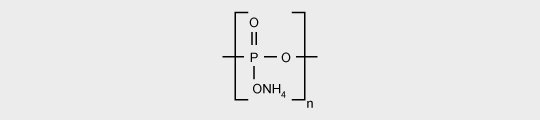
Ammonium polyphosphate (APP) is applied in intumescent formulations, polypropylene and thermosets such as unsaturated polyesters.
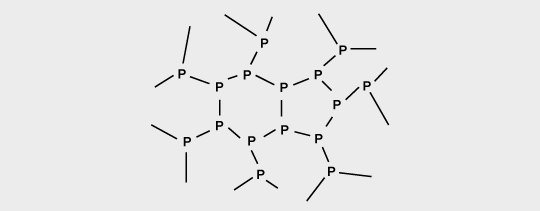
Red phosphorous is mostly used in polyamides.